Tattoo


A tattoo is a form of body modification, made by inserting indelible ink into the dermis layer of the skin to change the pigment.
Etymology

The word tattoo, or tattow in the 18th century, is a loanword from the Samoan word tatau, meaning "correct, workmanlike".[1] The Oxford English Dictionary gives the etymology of tattoo as "In 18th c. tattaow, tattow. From Polynesian (Tahitian, Samoan, Tongan, etc.) tatau. In Marquesan, tatu." Before the importation of the Polynesian word, the practice of tattooing had been described in the West as pricking, painting, or staining. Sailors on the voyage later introduced both the word and reintroduced the concept of tattooing to Europe.[2]
This is not to be confused with the origins of the word for the military drumbeat see military tattoo. In this case, the English word tattoo is derived from the Dutch word taptoe (OED).
The first written reference to the word tattoo (or Samoan tatau), appears in the journal of Joseph Banks (24 February 1743 19 June 1820), the naturalist aboard Captain Cook's ship the HMS Endeavour: "I shall now mention the way they mark themselves indelibly, each of them is so marked by their humor or disposition".
The word "tattoo" was brought to Europe by the explorer James Cook, when he returned in 1771 from his first voyage to Tahiti and New Zealand. In his narrative of the voyage, he refers to an operation called "tattaw". Before this it had been described as scarring, painting, or staining.[3]
Tattoo enthusiasts may refer to tattoos as "ink", "pieces", "skin art", "tattoo art", "tats", or "work"; to the creators as "tattoo artists", "tattooers", or "tattooists"; and to places where they work as "tattoo shops", "tattoo studios", or "tattoo parlors".

Usage of the terms "skin art", "tattoo art", "pieces", and work" is gaining greater support,[citation needed] with mainstream art galleries holding exhibitions of both conventional and custom tattoo designs. Beyond Skin, at the Museum of Croydon, is an example of this as it challenges the stereotypical view of tattoos and who has them. Copyrighted tattoo designs that are mass-produced and sent to tattoo artists are known as "flash", a notable instance of industrial design. Flash sheets are prominently displayed in many tattoo parlors for the purpose of providing both inspiration and ready-made tattoo images to customers.
The Japanese word irezumi means "insertion of ink" and can mean tattoos using tebori, the traditional Japanese hand method, a Western-style machine, or for that matter, any method of tattooing using insertion of ink. The most common word used for traditional Japanese tattoo designs is Horimono. Japanese may use the word "tattoo" to mean non-Japanese styles of tattooing.
Anthropologist Ling Roth in 1900 described four methods of skin marking and suggested they be differentiated under the names "tatu", "moko", "cicatrix", and "keloid".[4]
Types
The American Academy of Dermatology distinguishes five types of tattoos:[5] traumatic tattoos, also called "natural tattoos", that result from injuries, especially asphalt from road injuries or pencil lead; amateur tattoos; professional tattoos, both via traditional methods and modern tattoo machines; cosmetic tattoos, also known as "permanent makeup"; and medical tattoos.
Traumatic tattoos
| This section needs additional citations for verification. (November 2010) |
According to George Orwell, coal miners could develop characteristic tattoos owing to coal dust getting into wounds.[6] This can also occur with substances like gunpowder. Similarly, a traumatic tattoo occurs when a substance such as asphalt is rubbed into a wound as the result of some kind of accident or trauma. These are particularly difficult to remove as they tend to be spread across several layers of skin, and scarring or permanent discoloration is almost unavoidable depending on the location. An amalgam tattoo is when amalgam particles are implanted in to the soft tissues of the mouth, usually the gums, during dental filling placement or removal; another example of such accidental tattoos is the result of a deliberate or accidental stabbing with a pencil or pen, leaving graphite or ink beneath the skin.
Amateur and professional tattoos

Many tattoos serve as rites of passage, marks of status and rank, symbols of religious and spiritual devotion, decorations for bravery, sexual lures and marks of fertility, pledges of love, punishment, amulets and talismans, protection, and as the marks of outcasts, slaves and convicts. The symbolism and impact of tattoos varies in different places and cultures. Tattoos may show how a person feels about a relative (commonly mother/father or daughter/son) or about an unrelated person.[7] Today, people choose to be tattooed for artistic, cosmetic, sentimental/memorial, religious, and magical reasons, and to symbolize their belonging to or identification with particular groups, including criminal gangs (see criminal tattoos) or a particular ethnic group or law-abiding subculture. Some Mori still choose to wear intricate moko on their faces. In Cambodia, Laos, and Thailand, the yantra tattoo is used for protection against evil and to increase luck.[citation needed]
In the Philippines certain tribal groups believe tattoos have magical qualities, and help to protect their bearers. Most traditional tattooing in the Philippines is related to the bearer's accomplishments in life or rank in the tribe.[citation needed]
Extensive decorative tattooing is common among members of traditional freak shows and by performance artists who follow in their tradition.[citation needed]
Identification

People have also been forcibly tattooed. A well-known example is the identification system for inmates in Nazi concentration camps during The Holocaust. The Nazis introduced the practice of tattooing at Auschwitz in 1941 in order to identify the bodies of registered prisoners in the concentration camps. During registration, they would pierce the outlines of the serial-number digits onto the prisoners' arms. Tattoos have also been used for identification in other ways. As early as the Zhou, Chinese authorities would employ facial tattoos as a punishment for certain crimes or to mark prisoners or slaves. During the Roman Empire, Roman soldiers were required by law to have identifying tattoos on their hands in order to make desertion difficult. Gladiators and slaves were likewise tattooed: exported slaves were tattooed with the words "tax paid", and it was a common practice to tattoo "Stop me, I'm a runaway" on their foreheads.[citation needed] Owing in part to Biblical strictures against the practice, Emperor Constantine I banned tattooing the face around AD 330 and the Second Council of Nicaea banned all body markings as a pagan practice in AD 787.[8]

In the period of early contact between the Mori and Europeans, the Maori people hunted and decapitated each other for their moko tattoos, which they traded for European items including axes and firearms.[9] Moko tattoos were facial designs worn by women and men to indicate their lineage, social position, and status within the tribe. The tattoo art was a sacred marker of identity among the Maori and also referred to as a vehicle for storing one's tapu, or spiritual being, in the afterlife.[10]
Tattoos are sometimes used by forensic pathologists to help them identify burned, putrefied, or mutilated bodies. As tattoo pigment lies encapsulated deep in the skin, tattoos are not easily destroyed even when the skin is burned.[citation needed]
Tattoos are also placed on animals, though rarely for decorative reasons. Pets, show animals, thoroughbred horses, and livestock are sometimes tattooed with identification and other marks. Branding is used for similar reasons and is often performed without anesthesia, but is different from tattooing as no ink or dye is inserted during the process.[citation needed] Pet dogs and cats are sometimes tattooed with a serial number (usually in the ear, or on the inner thigh) via which their owners can be identified, though the use of a microchip has become the increasingly more popular choice.[citation needed]

Cosmetic
The cosmetic surgery industry continues to see a trend of increased popularity for both surgical and noninvasive procedures (Gimlin 2002; Sullivan 2001).
When used as a form of cosmetics, tattooing includes permanent makeup and hiding or neutralizing skin discolorations. Permanent makeup is the use of tattoos to enhance eyebrows, lips (liner and/or lipstick), eyes (liner), and even moles, usually with natural colors, as the designs are intended to resemble makeup.[citation needed]
A growing trend in the US and UK is to place artistic tattoos over the surgical scars of a mastectomy. "More women are choosing not to reconstruct after a mastectomy and tattoo over the scar tissue instead.... The mastectomy tattoo will become just another option for post cancer patients and a truly personal way of regaining control over post cancer bodies and proving once and for all that breast cancer is not just a pink ribbon."[11] The tattooing of nipples on reconstructed breasts remains in high demand, however.[12]

Functional
Functional tattoos are used primarily for a purpose other than aesthetics. One such use is to tattoo Alzheimer patients with their names, so they may be easily identified if they go missing.[13] Another example is a to-do list tattooed to someone's arm, as shown in the picture aside.
Medical
Medical tattoos are used to ensure instruments are properly located for repeated application of radiotherapy and for the areola in some forms of breast reconstruction. Tattooing has also been used to convey medical information about the wearer (e.g., blood group, medical condition, etc.). Additionally, tattoos are used in skin tones to cover vitiligo, a skin pigmentation disorder.[14]
SS blood group tattoos (German: Blutgruppentätowierung) were worn by members of the Waffen-SS in Nazi Germany during World War II to identify the individual's blood type. After the war, the tattoo was taken to be prima facie, if not perfect, evidence of being part of the Waffen-SS, leading to potential arrest and prosecution. This led a number of Ex-Waffen-SS to shoot themselves through the arm with a gun, removing the tattoo and leaving scars like the ones resulting from pox inoculation, making the removal less obvious.[citation needed]
Tattoos were probably also used in ancient medicine as part of the treatment of the patient. In 1898, Daniel Fouquet, a medical doctor, wrote an article on medical tattooing practices in Ancient Egypt, in which he describes the tattooed markings on the female mummies found at the Deir el-Bahari site. He speculated that the tattoos and other scarifications observed on the bodies may have served a medicinal or therapeutic purpose: "The examination of these scars, some white, others blue, leaves in no doubt that they are not, in essence, ornament, but an established treatment for a condition of the pelvis, very probably chronic pelvic peritonitis."[15]
History

Tattooing has been practiced for centuries in many cultures and spread throughout the world.[citation needed] The Ainu, an indigenous people of Japan, traditionally had facial tattoos, as did the Austroasians. Today, one can find Atayal, Seediq, Truku, and Saisiyat of Taiwan, Berbers of Tamazgha (North Africa), Yoruba, Fulani and Hausa people of Nigeria, and Mori of New Zealand with facial tattoos.[citation needed] Tattooing was popular among certain ethnic groups in southern China, Polynesia, Africa, Borneo, Cambodia, Europe, Japan, the Mentawai Islands, MesoAmerica, New Zealand, North America and South America, the Philippines, Iron Age Britain, and Taiwan.[citation needed]

It is a myth that the modern revival of tattooing stems from Captain James Cook's three voyages to the South Pacific in the late 1700s.[16] Certainly, Cook's voyages and the dissemination of the texts and images from them brought more awareness about tattooing (and, as noted above, imported the word "tattow" into Western languages), but Europeans have gotten tattooed throughout history. On Cook's first voyage in 1768, his science officer and expedition botanist, Sir Joseph Banks, as well as artist Sydney Parkinson and many others of the crew, returned to England with tattoos, although many of these men would have had pre-existing tattoos. Banks was a highly regarded member of the English aristocracy and had acquired his position with Cook by putting up what was at the time the princely sum of some ten thousand pounds in the expedition. In turn, Cook brought back with him a tattooed Raiatean man, Omai, whom he presented to King George and the English Court. On subsequent voyages other crew members, from officers, such as American John Ledyard to ordinary seamen, got tattooed.
As many tattoos were stimulated by Polynesian and Japanese examples, amateur tattoo artists[17] were in great demand in port cities all over the world, especially by European and American sailors. The first documented professional tattoo artist in the US was Martin Hildebrandt, a German immigrant who arrived in Boston in 1846. Between 1861 and 1865, he tattooed soldiers on both sides in the American Civil War.[18] The first documented professional tattooist in Britain was established in the port of Liverpool in the 1870s. In Britain tattooing was still largely associated with sailors[19] and the lower or even criminal class,[20] but by the 1870s had become fashionable among some members of the upper classes, including royalty,[3][21] and in its upmarket form it could be an expensive[22] and sometimes painful[23] process. A marked class division on the acceptability of the practice continued for some time in Britain.[24]
Since the 1970s, tattoos have become a mainstream part of Western fashion, common among both sexes, to all economic classes, and to age groups from the later teen years to middle age. For many young Americans, the tattoo has taken on a decidedly different meaning than for previous generations. The tattoo has "undergone dramatic redefinition" and has shifted from a form of deviance to an acceptable form of expression.[25] In 2010, 25% of Australians under age 30 had tattoos.[26]
Process

 Play media
Play media
Tattooing involves the placement of pigment into the skin's dermis, the layer of dermal tissue underlying the epidermis. After initial injection, pigment is dispersed throughout a homogenized damaged layer down through the epidermis and upper dermis, in both of which the presence of foreign material activates the immune system's phagocytes to engulf the pigment particles. As healing proceeds, the damaged epidermis flakes away (eliminating surface pigment) while deeper in the skin granulation tissue forms, which is later converted to connective tissue by collagen growth. This mends the upper dermis, where pigment remains trapped within fibroblasts, ultimately concentrating in a layer just below the dermis/epidermis boundary. Its presence there is stable, but in the long term (decades) the pigment tends to migrate deeper into the dermis, accounting for the degraded detail of old tattoos.[27]
Some tribal cultures traditionally created tattoos by cutting designs into the skin and rubbing the resulting wound with ink, ashes or other agents; some cultures continue this practice, which may be an adjunct to scarification. Some cultures create tattooed marks by hand-tapping the ink into the skin using sharpened sticks or animal bones (made like needles) with clay formed disks or, in modern times, needles.
The most common method of tattooing in modern times is the electric tattoo machine, which inserts ink into the skin via a single needle or a group of needles that are soldered onto a bar, which is attached to an oscillating unit. The unit rapidly and repeatedly drives the needles in and out of the skin, usually 80 to 150 times a second. This modern procedure is ordinarily sanitary. The needles are single-use needles that come packaged individually. The tattoo artist must wash his or her hands and must also wash the area that will be tattooed. Gloves must be worn at all times and the wound must be wiped frequently with a wet disposable towel of some kind. The equipment must be sterilized in a certified autoclave before and after every use.
Associations

The Government of Meiji Japan had outlawed tattoos in the 19th century, a prohibition that stood for 70 years before being repealed in 1948.[28] As of June 6, 2012 all new tattoos are forbidden for employees of the city of Osaka. Existing tattoos are required to be covered with proper clothing. The regulations were added to Osaka's ethical codes, and employees with tattoos were encouraged to have them removed. This was done because the strong connection of tattoos with the yakuza, or Japanese organized crime, after an Osaka official in February 2012 threatened a schoolchild by showing his tattoo.
Tattoos had negative connotations in historical China, where criminals often had been marked by tattooing.[29][30] The association of tattoos with criminals was transmitted from China to influence Japan.[29] Today, tattoos have remained a taboo in Chinese society.[31]
Current cultural understandings of tattoos in Europe and North America have been greatly influenced by long-standing stereotypes based on deviant social groups in the 19th and 20th centuries. Particularly in North America tattoos have been associated with stereotypes, folklore, and racism.[10] Not until the 1960s and 1970s did people associate tattoos with such societal outcasts as bikers and prisoners.[32] Today, in the United States many prisoners and criminal gangs use distinctive tattoos to indicate facts about their criminal behavior, prison sentences, and organizational affiliation.[33] A teardrop tattoo, for example, can be symbolic of murder, or each tear represents the death of a friend. At the same time, members of the U.S. military have an equally well-established and longstanding history of tattooing to indicate military units, battles, kills, etc., an association that remains widespread among older Americans. Tattooing is also common in the British Armed Forces. A study conducted in 2004 among 500 adults between ages 18 and 50 found an explicit link between tattooing and criminality. 72 percent of respondents with face, neck, hands, or fingers tattoos have spent more than three days in jail, compared to 6 percent of the non-tattooed population.[34][35] Depending on vocation tattoos are accepted in a number of professions in America. Companies across many fields are increasingly focused on diversity and inclusion.[36]
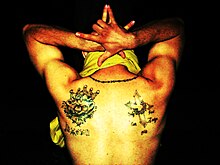
The Romans tattooed criminals and slaves, and in the 19th century released US convicts and British army deserters were identified by tattoos. Prisoners in Siberian and Nazi concentration camps were tattooed with an identification number. Today, many prison inmates still tattoo themselves as an indication of time spent in prison.[3]
Native Americans also used tattoos to represent their tribe. Catholic Croats of Bosnia used religious Christian tattooing, especially of children and women, for protection against forced conversion to Islam during the Ottoman occupation of the Balkans.[37]
Insofar as this cultural or subcultural use of tattoos predates the widespread popularity of tattoos in the general population, tattoos are still associated with criminality. Tattoos on the face in the shape of teardrops are usually associated with how many people a person has murdered. Although the general acceptance of tattoos is on the rise in Western society, they still carry a heavy stigma among certain social groups. Tattoos are generally considered an important part of the culture of the Russian mafia.

The prevalence of women in the tattoo industry, along with larger numbers of women bearing tattoos, appears to be changing negative perceptions. A study of "at-risk" (as defined by school absenteeism and truancy) adolescent girls showed a positive correlation between body modification and negative feelings towards the body and low self-esteem; however, the study also demonstrated that a strong motive for body modification is the search for "self and attempts to attain mastery and control over the body in an age of increasing alienation".[38]
Many studies have been done of the tattooed population and society's view of tattoos. In June 2006, the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology published the results of a telephone survey of 2004. It found that 36% of Americans ages 1829, 24% of those 3040, and 15% of those 4151 had a tattoo.[34] In September 2006, the Pew Research Center conducted a telephone survey that found that 36% of Americans ages 1825, 40% of those 2640 and 10% of those 4164 had a tattoo. They concluded that Generation X and Generation Y are not afraid to express themselves through their appearance, and tattoos are the most popular form of self-expression.[39] In January 2008, a survey conducted online by Harris Interactive estimated that 14% of all adults in the United States have a tattoo, slightly down from 2003, when 16% had a tattoo. Among age groups, 9% of those ages 1824, 32% of those 2529, 25% of those 3039 and 12% of those 4049 have tattoos, as do 8% of those 5064. Men are slightly more likely to have a tattoo than women.
Advertising and marketing
Tattoos have also been used in marketing and advertising with companies paying people to have logos of brands like HBO, Red Bull, ASOS.com, and Sailor Jerry's rum tattooed in their bodies.[40] This practice is known as "skinvertising".[41]
B.T.'s Smokehouse, a barbecue restaurant located in Massachusetts, offered customers free meals for life if they had the logo of the establishment tattooed on a visible part of their bodies. Nine people took the business up on the offer.[42]
Health risks

Because it requires breaking the skin barrier, tattooing carries health risks including infection and allergic reactions. Modern tattooists reduce risks by following universal precautions working with single-use items and sterilizing their equipment after each use. Many jurisdictions require that tattooists have blood-borne pathogen training such as that provided through the Red Cross and OSHA. As of 2009 (in the United States) there have been no reported cases of HIV contracted from tattoos.[43]
In amateur tattooing, such as that practiced in prisons, however, there is an elevated risk of infection. Infections that can theoretically be transmitted by the use of unsterilized tattoo equipment or contaminated ink include surface infections of the skin, fungal infections, some forms of hepatitis, herpes simplex virus, HIV, staph, tetanus, and tuberculosis.[44]
Tattoo inks have been described as "remarkably nonreactive histologically".[27] However, cases of allergic reactions to tattoo inks, particularly certain colors, have been medically documented. This is sometimes due to the presence of nickel in an ink pigment, which triggers a common metal allergy. Occasionally, when a blood vessel is punctured during the tattooing procedure, a bruise/hematoma may appear.
Removal
While tattoos are considered permanent, it is sometimes possible to remove them, fully or partially, with laser treatments. Typically, black and some colored inks can be removed more completely than inks of other colors. The expense and pain associated with removing tattoos are typically greater than the expense and pain associated with applying them. Pre-laser tattoo removal methods include dermabrasion, salabrasion (scrubbing the skin with salt), cryosurgery, and excisionwhich is sometimes still used along with skin grafts for larger tattoos. These older methods, however, have been nearly completely replaced by laser removal treatment options.[45]
Temporary tattoos

Ink or coloring applied to the surface of skin is sometimes referred to as a "tattoo". Mehndi, also known as a henna, is a traditionally Hindu method of staining the skin. Modern techniques include ink transfers on sheets of paper.
See also
Styles
- Black-and-gray
- Body suit (tattoo)
- Borneo traditional tattooing
- Criminal tattoo
- Irezumi, traditional Japanese tattoo
- Finger moustache tattoo
- Genital tattooing
- Lower back tattoo
- Marquesan tattoo
- Old school (tattoo)
- Pet tattoo
- Sailor tattoos
- Scarification
- SS blood group tattoo
- Swallow tattoo
- Calligraphy tattoo
- Watercolor
Others
- Biomechanical art
- Foreign body granuloma
- Legal status of tattooing in the United States
- List of cutaneous conditions
- List of tattoo artists
- Lucky Diamond Rich, world's most tattooed person.
- Tattoo convention
References
Bibliography
- Anthropological
- Buckland, A. W. (1887) "On Tattooing", in Journal of the Royal Anthropological Institute of Great Britain and Ireland, 1887/12, p. 318328
- Caplan, Jane (ed.) (2000): Written on the Body: the Tattoo in European and American History, Princeton University Press
- DeMello, Margo (2000) Bodies of Inscription: a Cultural History of the Modern Tattoo Community, California. Durham NC: Duke University Press
- Fisher, Jill A. (2002). "Tattooing the Body, Marking Culture". Body & Society 8 (4): pp. 91107.
- Gell, Alfred (1993) Wrapping in Images: Tattooing in Polynesia, Oxford: Clarendon Press
- Gilbert, Stephen G. (2001) Tattoo History: a Source Book, New York: Juno Books
- Gustafson, Mark (1997) "Inscripta in fronte: Penal Tattooing in Late Antiquity", in Classical Antiquity, April 1997, Vol. 16/No. 1, p. 79105
- Hambly, Wilfrid Dyson (1925) The History of Tattooing and Its Significance: With Some Account of Other Forms of Corporal Marking, London: H. F. & G. Witherby (reissued: Detroit 1974)
- Hesselt van Dinter, Maarten (2005) The World of Tattoo; An Illustrated History. Amsterdam, KIT Publishers
- Jones, C. P. (1987) "Stigma: Tattooing and Branding in GraecoRoman Antiquity", in Journal of Roman Studies, 77/1987, pp. 139155
- Juno, Andrea. Modern Primitives. Re/Search #12 (October 1989) ISBN 0-9650469-3-1
- Kächelen, Wolf-Peter (2004): Tatau und Tattoo Eine Epigraphik der Identitätskonstruktion. Shaker Verlag, Aachen, ISBN 3-8322-2574-9.
- Lombroso, Cesare (1896) "The Savage Origin of Tattooing", in Popular Science Monthly, Vol. IV., 1896
- Pang, Joey (2008) "Tattoo Art Expressions", http://www.tattootemple.hk
- Raviv, Shaun (2006) "Marked for Life: Jews and Tattoos" (Moment Magazine; June 2006)
- "Comparative study about Ötzi's therapeutic tattoos" (L. Renaut, 2004, French and English abstract)
- Robley, Horatio (1896) Moko, or, Maori tattooing. London: Chapman and Hall
- Roth, H. Ling (1901) "Maori tatu and moko". In: Journal of the Anthropological Institute vol. 31, JanuaryJune 1901
- Rubin, Arnold (ed.) (1988) Marks of Civilization: Artistic Transformations of the Human Body, Los Angeles: UCLA Museum of Cultural History
- Sanders, Clinton R. (1989) Customizing the Body: the Art and Culture of Tattooing. Philadelphia: Temple University Press
- Sinclair, A. T. (1909) "Tattooing of the North American Indians", in American Anthropologist 1909/11, No. 3, p. 362400
- Wianecki, Shannon (2011) "Marked" Maui No Ka 'Oi Magazine.
- Popular and artistic
- Green, Terisa. Ink: The Not-Just-Skin-Deep Guide to Getting a Tattoo ISBN 0-451-21514-1
- Green, Terisa. The Tattoo Encyclopedia: A Guide to Choosing Your Tattoo ISBN 0-7432-2329-2
- Krakow, Amy. Total Tattoo Book ISBN 0-446-67001-4
- Medical
- CDC's Position on Tattooing and HCV Infection, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, retrieved June 12, 2006
- Body Art (workplace hazards), National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health, retrieved September 15, 2008
- "Tattoos and Permanent Makeup", CFSAN/Office of Cosmetics and Colors (2000; updated 2004, 2006) (United States Food and Drug Administration), retrieved June 12, 2006
Haley, R. P.; Fischer (March 2000). "Commercial tattooing as a potential source of hepatitis C infection". Medicine 80: 134151.
Notes
- ^ Samoa: Samoan Tattoos, Polynesian Cultural Center
- ^ tattoo 2. The American Heritage® Dictionary of the English Language: Fourth Edition. 2000
- ^ a b c "tattoo". The Hutchinson Unabridged Encyclopedia with Atlas and Weather guide (Credo Reference. Web. ed.). Helicon. 17 September 2012.
- ^ Roth, H. Ling (11 September 1900). On Permanent Artificial Skin Marks: a definition of terms. Bradford: Anthropological Section of the British Association for the Advancement of Science.
- ^ "Tattoos, Body Piercings, and Other Skin Adornments". Aad.org. Retrieved 2012-04-05.
- ^ George Orwell (1940). "Down the Mine". Inside the Whale.
- ^ Johnson, Frankie J. "Tattooing: Mind, Body And Spirit. The Inner Essence Of The Art". Sociological Viewpoints 23. (2007): 4561. Academic Search Premier. Web. 13 Mar. 2013.
- ^ Adrienne Mayor (MarchApril 1999). "People Illustrated". Archaeological Institute of America 52 (2).
- ^ A Strange Trade - Deals in Maori Heads
- ^ a b Michael Atkinson. Tattooed: the sociogenesis of a body art. Retrieved 2012-04-05.
- ^ Locke, Katherine. 2013. "Women choose body art over reconstruction after cancer battle: Undergoing a mastectomy is a harrowing experience, but tattoos can celebrate the victory over cancer." The Guardian. August 7, 2013.
- ^ "Nipple tattoos and their Michelangelo". BBC News. 2013-12-21.
- ^ Hürriyet Daily News: Tattooist offers to tattoo names of Alzheimer patients in İzmir
- ^ Arndt, Kenneth A.; Hsu, Jeffrey T. S. (2007). Manual of Dermatologic Therapeutics (illustrated ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 116. ISBN 978-0781760584. Retrieved 2013-09-06.
- ^ Tattooing in Ancient Egypt Part 2: The Mummy of Amunet by Gemma Angel, on 10 December 2012.
- ^ http://tattoohistorian.com/2014/04/05/the-cook-myth-common-tattoo-history-debunked/
- ^ During the Tichborne case, a witness, Lord Bellew, testified he and the missing Roger Tichborne tattooed each other while they were both schoolboys at Stonyhurst College. Tichborne left school in 1848. The Times (London), 2 February 1872, p. 10
- ^ Steward, Samuel M. (1990). Bad Boys and Tough Tattoos: A Social History of the Tattoo with Gangs, Sailors, and Street-corner Punks, 19501965. Psychology Press. ISBN 978-1560240235. Retrieved 2013-09-06.
- ^ Some days after a shipwreck divers recovered the bodies. Most were unrecognisable, but that of a crew member was readily identified by his tattoos: "The reason why sailors tattoo themselves has often been asked." The Times (London), 30 January 1873, p. 10
- ^ The Times (London), 3 April 1879, p. 9: "Crime has a ragged regiment in its pay so far as the outward ... qualities are concerned ... they tattoo themselves indelibly ... asserting the man's identity with the aid of needles and gunpowder. This may be the explanation of the Mermaids, the Cupid's arrows, the name of MARY, the tragic inscription to the memory of parents, the unintended pathos of the appeal to liberty."
- ^ Broadwell, Albert H. (27 January 1900). "Sporting pictures on the human skin". Country Life. Article describing work of society tattooist Sutherland Macdonald refers to his clientele including "members of our Royal Family, among them H.R.H. the Duke of York, H.I.M. the Czarevitch, and Imperial and Royal members of Russian, German and Spanish courts...."
- ^ The Times (London), 18 April 1889, p. 12: "A Japanese Professional Tattooer". Article describes the activities of an unnamed Japanese tattooist based in Hong Kong. He charged £4 for a dragon, which would take 5 hours to do. The article ends "The Hong-Kong operator tattooed the arm of an English Prince, and, in Kioto, was engaged for a whole month reproducing on the trunk and limbs of an English peer a series of scenes from Japanese history. For this he was paid about £100. He has also tattooed ladies.... His income from tattooing in Hong Kong is about £1,200 per annum."
- ^ Broadwell, Albert H. (27 January 1900). "Sporting pictures on the human skin". Country Life. "In especially sensitive cases a mild solution of cocaine is injected under the skin, ... and no sensation whatever is felt, while the soothing solution is so mild that it has no effect ... except locally."
- ^ In 1969 the House of Lords debated a bill to ban the tattooing of minors, on grounds it had become "trendy" with the young in recent years but was associated with crime, 40 per cent of young criminals having tattoos. Lord Teynham and the Marquess of Aberdeen and Temair however rose to object that they had been tattooed as youngsters, with no ill effects. The Times (London), April 29, 1969, p. 4: "Saving young from embarrassing tattoos".
- ^ Roberts, D. J. (2012). "Secret Ink: Tattoo's Place in Contemporary American Culture". Journal of American Culture 35 (2): 15365. doi:10.1111/j.1542-734x.2012.00804.x.
- ^ Brittany, By (2010-10-31). "I'm inked therefore I am: Why tatts have left a mark on Gen Y". News.com.au. Retrieved 2012-04-05.
- ^ a b Tattoo lasers / Histology, Suzanne Kilmer, eMedicine
- ^ Ito, Masami, "Whether covered or brazen, tattoos make a statement", Japan Times, June 8, 2010, p. 3
- ^ a b DeMello, Margo (2007). Encyclopedia of body adornment. Westport: Greenwood Press. p. 61. ISBN 978-0-313-33695-9.
- ^ Dutton, Michael (1998). Streetlife China. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 163 & 180. ISBN 0-521-63141-6.
- ^ Dutton, Michael (1998). Streetlife China. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. p. 180. ISBN 0-521-63141-6.
- ^ Bodies of Inscription: A Cultural History of the Modern Tattoo Community. Margo DeMello. Durham, NC: Duke University Press, 2000. vii + 222 pp., photographs, notes, bibliography, index.
- ^ Andrew Lichtenstein, Texas Prison Tattoos, retrieved 2007-12-08
- ^ a b Laumann, Anne E.; Derick, Amy J. (September 2006). "Tattoos and Body Piercings in the United States: A National Data Set". Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 55 (3): 413421. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2006.03.026. PMID 16908345.
- ^ Joshua Adams (2012), "The Relationship between Tattooing and Deviance in Contemporary Society", Deviance Today: 137145
- ^ Hennessey, Rachel (2013-03-08). "Tattoos No Longer A Kiss Of Death In The Workplace - Yahoo! Small Business Advisor". Smallbusiness.yahoo.com. Retrieved 2013-03-15.
- ^ Truhelka, Ciro. Wissenschaftliche Mittheilungen Aus Bosnien und der Hercegovina: "Die Tätowirung bei den Katholiken Bosniens und der Hercegovina." Sarajevo; Bosnian National Museum, 1896.
- ^ Carroll, L.; Anderson, R. (2002), "Body piercing, tattooing, self-esteem, and body investment in adolescent girls", Adolescence 37 (147): 62737, PMID 12458698
- ^ "A Portrait of "Generation Next"". The Pew Research Center for the People and the Press. Retrieved 2012-04-05.
- ^ Allen, Kevin (2013-06-25). "Your ad here? Marketers turn to tattoos". PR Daily (Ragan Communications, Inc.). Retrieved 2014-04-18.
- ^ Hines, Alice (2013-05-30). "The Tattoo As Corporate Branding Tool". Details (Condé Nast.). Retrieved 2014-04-18.
- ^ Boynton, Donna (2013-02-19). "B.T.'s Smokehouse logo tattoo earns patrons free meals for life". Telegram.com (Worcester Telegram & Gazette Corp.). Retrieved 2014-04-18.
- ^ "HIV and Its Transmission". CDC. July 1999.
- ^ "Tattoos: Risks and precautions to know first". MayoClinic.com. 2012-03-20. Retrieved 2012-04-05.
- ^ Images of Tattoo removal procedure, retrieved 2011-01-12
External links
| Wikisource has the text of The New Student's Reference Work article Tattooing. |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to tattoos. |
- Tattoos, The Permanent Art Documentary produced by Off Book (web series)
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
- Tattooing
- 1970s fashion
- 1980s fashion
- 1990s fashion
- 2000s fashion
- 2010s fashion
- Samoan words and phrases
- Skin conditions resulting from physical factors
ConversionConversion EmoticonEmoticon